The global sports betting market is extremely attractive for both legal entities and black-market operators. The bookmaking industry creates hundreds of thousands of jobs, allows for sustainable development of the iGaming market, and has many other benefits. At the same time, it also creates a risk of corruption, money laundering, fraud, and unlicensed gambling. This can lead to negative consequences in both sports and gambling sectors.
In the modern digital world, the online sector of the betting market is also rapidly growing. While this allows for creating a more engaging experience for the player, it also generates new opportunities for illegal operators.
Legalization of the gambling and betting activities is a big trend in recent years. Most of the EU states officially recognize sportsbooks and work to combat illicit activities in the market. According to EGBA, by 2026, offshore operators would account only for 12% of all the European online gambling market. Black-market sportsbooks, however, will always find a way to circumvent the restrictions and provide bettors with attractive offers. So, how does the trend for legal bookmakers affects black and grey market operators? And, more importantly, will illegal sportsbooks eventually go extinct, or will they remain a crucial part of the sports betting industry? Keep reading to find out.
Overview of the current situation in the sports betting market
The joint study by the UN and Asian Racing Federation states that there are three main types of sportsbook operators:
- White-market companies;
- Grey-market companies;
- Black-market companies.
While the first type of betting activity is completely legal and is performed by corporate citizens, grey- and black-market wagering activities are considered illegal, with black companies being run by criminals. Black and grey market sportsbooks also often overlap.

Legal sports betting is on the rise
Over the past decade, the legal sports betting market has grown significantly. The UN experts calculated that in 2020, the regulated sportsbook sector was worth around $40 billion. As for the betting regions, people in Asia ($19.6bn), Europe ($15.2bn), and North America ($2.3bn) tend to wager the most with the legal operators.
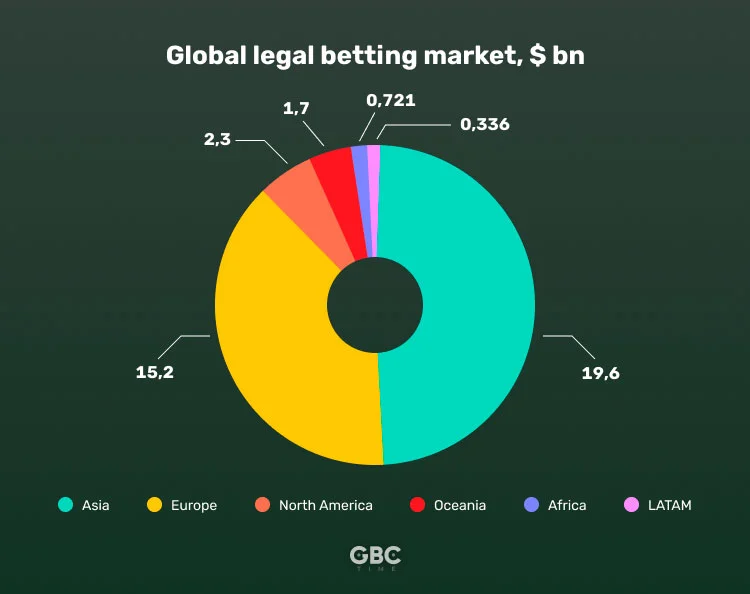
There are, however, new legal markets emerging every year, so the picture could drastically change, once Brazil (which is huge for sports betting) finally adopts the online gambling law.
In 2018, the US Supreme Court allowed state governments to authorize sports betting for commercial purposes, ending the 26-year-long ban. The European countries follow this trend:
- In the summer of 2020, Ukraine legalized gambling, which was illegal since 2009;
- In the summer of 2021, Germany allowed online gambling on the national scale;
- In autumn 2021, the Netherlands launched the iGaming market, ending the monopoly of Holland Casino.
These are only a few cases that have had a significant impact on the global betting scene.
It is also important to understand that the bookmaking industry is closely intertwined with sportsmanship, TV broadcasting, etc.
Main reasons for the expansion of the legal sportsbook market
The main factors that contribute to the growth of the legal bookmaking are:
- Growing Internet penetration. Statista reports that by 2025, there will be over 5.6 Internet users on the planet. Currently, 63% of the global population (4.9 billion people) has an access to the Internet. Meanwhile, Asia has the highest number of online users (60% of all), while Europe has the highest penetration rate (98% in the Northern part and 94% in the Western part).
- Increasing usage of mobile devices. Mobile betting is the other important trend that impacts the global betting outlook. With more and more people preferring to gamble on their pocket devices, legal sportsbooks tend to adapt to the demand and go mobile. EGBA reports that in 2021, over half (50.5%) of all online bets in Europe were placed from a mobile device.;
- Accessibility of online betting. Remote betting is a new trend, which became especially hot at the beginning of the global pandemic in 2020. Millions of gamblers prefer to bet in the comfort of their own home without needing to go to the betting shop or a casino;
- Improved social attitude towards gambling. With the legalization of betting activities, the stigma around betting on sports begins to fade. While it is still considered a harmful activity, more and more people view gambling as just a pastime, taking into account its legal status;
- Corporate sponsorships and celebrity endorsements. Many famous sportsbook brands hire sports stars to promote their brand. The most well-known cases are Christiano Ronaldo’s deal with PokerStars and Conor McGregor’s collaboration with Parimatch. Some countries like the UK, however, plan to ban celebrity sponsorships in an attempt to protect minors and other vulnerable groups.
The scope of Illegal betting is shocking, experts say
While the number of regulated sportsbooks is constantly growing, the scale of illicit activities in the betting sphere is also grand. The UN estimates that the total turnover illegal sports betting market reaches $1.7 trillion each year and is not less than $1 trillion. At the same time, the legal market is estimated to have a $474 billion total turnover.
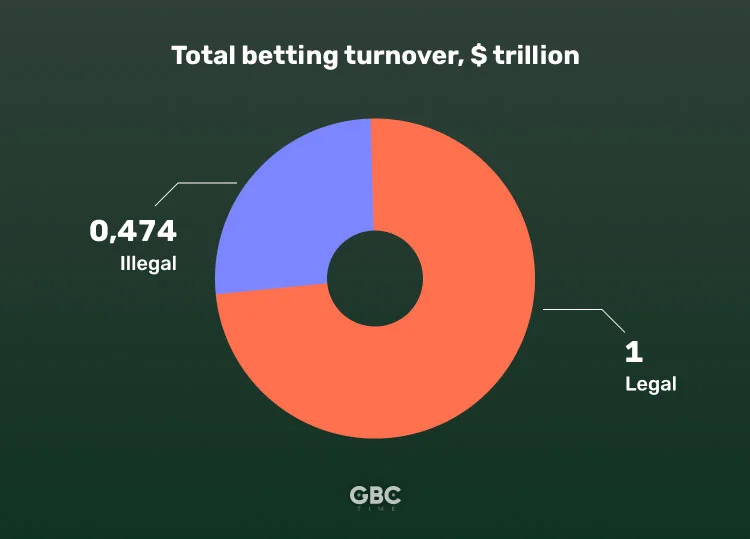
So, the illegal market is at least double the size of the regulated betting market. It also shows the great potential for the growth of legal bookmaking, given the right circumstances.
Nowadays, illegal betting takes place in:
- black markets, where operators do not have any gambling permit and are considered organizers of a crime;
- offshore sportsbook markets where ops hold a betting license of a single jurisdiction (Curacao or Malta) but offer their services to other regions, where they do not have a license.
Key growth drivers for the black betting market
The global shift of the gambling industry to online, which happened in the past few years, not only stipulated legal sports betting. As stated in the Delloite report: “The ability to place wagers virtually as opposed to in-person is crucial to the development of the market.”
It was also the main growth driver for the black sportsbooks market. The ability to place bets online allowed sportsbooks to reach new audiences with ease. Bettors no longer had to be physically located in the same place as the operator. The ability to place a wager instantly and the accessibility of electronic payments also contributed to the cause. Additionally, users could just use VPN or mirror sites to access the black-market sportsbook, even if the website is blocked in their country. So, with the greater Internet penetration, black market sportsbooks became a global problem instead of a local issue of each gambling market.
The other reasons for the constant growth of black-market betting are:
- The globalization of sports viewership. Nowadays, millions of people can tune in for their favorite game online or watch the TV broadcast. Consequently, some of these sports fans want to bet on the team they like;
- The popularity of betting in countries, where sports betting is limited. Brazil is the most prominent example of this. While Brazilians are known to be avid sports fans and betting enthusiasts, the local government does not permit online betting. So, the bettors have no other choice but to go to the offshore or black-market wagering websites.
- Loopholes in the gambling jurisdictions. Some countries do not specifically outlaw offshore betting or have other gaps in their iGaming legislation, which allows illegal sportsbooks freely operate in the country. Black-market bookmakers often flourish in the states, where legal authorities cannot easily spot their activity due to problems in the legal framework or political regime;
- Public forums and social media. The advertising for black market sportsbooks is typically posted online, on social networks, like Facebook, Reddit, Instagram, etc. Targeted advertising plays a key role in the affiliate promotion of illegal bookmakers. Additionally, Illicit sports betting often takes place on messaging platforms, which facilitate peer-to-peer communications, real-time wagering, and private discussions;
- Anonymity. While most legal sportsbooks require identity verifications, black-market bookmakers exploit the anonymity of the web and cryptos.
Threats posed by illegal betting
At the same time, unlicensed betting is dangerous to the players, regular people, and the financial markets of the countries they operate in. It has already become a global problem, recognized by many states. The variety of bet types, the spread of online sports betting, and the common use of cryptocurrencies by remote sportsbooks only intensify the issue. As digital assets allow for secure yet untraceable transactions, they are often used for unlicensed betting, money laundering, and terrorist financing.
The UN report states that sports betting is often used for the following illicit activities:
- Money laundering – criminals take advantage of the bookmaking services;
- Corruption in sport, including manipulation in competitions;
- Selling compromised accounts of sports betting companies;
- Hacking prominent sportsbook ops;
- Organization of illegal wagering on sports.
Money laundering is an especially big concern for governments, sports organizations, and gambling authorities across the globe. Experts estimate that criminals launder about $800 billion – $2 trillion each year, which amounts to 2-5% of global gross domestic product.
As for the influence on the players, black-market sportsbooks do not offer any responsible gaming programs or any player protection. So, the gamblers who are susceptible to gambling harm are left alone with their problems.
How legalization of betting affects black markets?
As established earlier, the legalization of sportsbooks is an inevitable trend that shapes the way the betting market looks today. In the last 20-30 years, most countries have adopted some form of regulation for sports betting.
To understand how the legal offer influences black- and grey-market sportsbooks, we analyzed the most common positive and negative effects.
| Positive | Negative |
| Availability of legal offers leads to lower demand on black markets. | Imperfections in the licensing system can lead to abuse from illicit ops. |
| The legalization of sports betting can induce more celebrity sponsorships, thus, promoting legal offers. | Overregulation can fuel black markets. |
So, let us delve into the effect legal sports betting has on black-market activities.
The accessible legal offer reduces black-market activity
Overall, the legalization of sports betting has a positive effect on the gambling market, reducing the scope of illegal activities while providing players with safe betting options. Typically, when provided with legal bookmaking options, players tend to switch from black and grey markets.
Recent data from the American Gaming Association (AGA) proves that. After the legal approval of sportsbooks in 2018, demand for regulated sportsbooks in the US drastically increased. The 2020 research found out that 74% of American gamblers now want to bet only with legal sportsbooks.
This all, however, only takes place if the regulations in the sports betting sector do not prevent legal operators from competing with offers in the black market.
The marketing of regulated bookmakers also plays an important role, as many bettors simply confuse legal and black-market operators. This is where gambling sponsorships come to prominence.
More sponsorships mean higher visibility of legal brands
The legalization of sports betting activities also leads to the massive growth of gambling sponsorships. Bookmaking sponsorships are especially popular in sports leagues. Here, you can read how much EPL clubs earn from front-of-shirt deals.
Not all brands, however, agree to associate with gambling businesses. Some financial companies, for instance, do not sign betting sponsorship deals. Besides, several European regulators try to curb this form of promotion. For instance, the UK plans to outlaw front-of-shirt sponsorships in 2023.
Nonetheless, the betting sponsorships increase the visibility of legal brands, which leads to the growth of the regulated markets. And, consequently, lowers the demand for illegal and offshore bookmakers.
Flaws in the licensing system enable grey market bookmakers
It is important to understand that illicit activities take place in both grey and black betting markets. And while black-market ops were present even before online gambling, grey market sportsbooks emerged with the creation of the first Internet sportsbooks.
Internet-based betting brought great convenience to both organizers and players of games of chance. At the same time, it created many difficulties from the regulatory perspective. While some counties allow online betting and hand out sportsbook licenses to nearly anyone, other states ban online gambling activities. Naturally, some bookmaking companies take advantage of this uneven regulatory landscape.
Nowadays, it is relatively easy to start an online gambling business. So, some betting operators obtain a license from one jurisdiction (for instance, Curacao or Malta) and promote and offer their services to players in countries where sportsbooks are illegal. And as there is no universal regulatory system in the field of iGaming, authorities cannot effectively penalize and restrict these operators. With so many sportsbooks offering their services in multiple jurisdictions at one time, it becomes extremely hard to monitor if they are licensed in one particular market. Moreover, when confronted, grey market companies claim that they did nothing wrong as they have a betting license.
Overregulation can fuel the black-market activity
The other issue with the legalization of sports betting is overregulation. Numerous gambling market experts have argued that overly restrictive gambling laws only lead to the growth of black-market activity. When faced with tight limitations, like deposit or stake caps, ban on gambling ads, high tax rates, etc., legal operators have no other choice but to alter their offer to comply with the regulations. This, however, makes the legal sportsbooks less attractive for the players, who then switch to illegal sportsbooks with better odds and no betting limits.
Germany
The European market of Germany and Sweden could be great examples of this. In July 2021, Germany has adopted a State Treaty on Gambling, allowing an unlimited number of sports betting operators to register in the country. At the same time, the law includes a number of rigorous regulations:
- A ban on live streaming on sportsbook sites;
- In-play betting is limited to the final score and associated market (this point, however, is unclear);
- A 1-minute delay when a player switches between sports betting and slots on one website;
- A 5-minute delay when a player switches between betting sites.
While the legalization of betting could present competition to black market providers, iGaming expert Martin Lycka believes that the restrictive nature of the new law will only invigorate illegal operators. With legal sportsbooks being unable to present competitive offers to the bettors, Germans will move to black markets.
The data from the German trade body Deutscher Sportwettenverband (DSWV) confirms this trend and shows the shocking size of illegal gambling in the country. As of February 2022, there were 507 unlicensed gambling websites, compared to 36 legal providers in Germany.

Sweden
The situation in Sweden is similar. The country legalized online gambling in 2019. In 2020, the Swedish regulator, however, imposed strict limitations on the gambling sector, including SEK5 000 weekly deposit limit. This resulted in the player channelization dropping from 95% to 75% in just one year (from 2019 to 2020).
The Trade Association iGaming in Sweden (BOS) also found out that 7% of local gamblers played at an unlicensed website at least once. Moreover, 20% of those did so to avoid self-exclusion measures and 16% – to avoid a wagering limit. This clearly shows the link between strict regulations and the growth of the black market.
An unclear definition of illegal betting could lead to the growth of the illegal market
As stated previously, there is no universal definition for illegal sports betting. That is why many black-market sportsbooks abuse this imperfect system.
The EU has the most progressive regulation in that matter. In 2014, the European Convention on the Manipulation of Sports Competition Council approved a definition of illegal betting, which means any bookmaking activity, the type or operator of which is not permitted under the law of the country where the player is located. The definition, however, is not perfect and contradicts the gambling legislation of some EU states like Malta. According to the local laws, operators that hold an EU license can offer their services in the country. So, betting ops with a Maltese license believe they can operate in Finland, where the state-regulated company holds a monopoly on gambling. So, a range of grey market ops takes advantage of this loophole.
The same situation occurs in America and the Caribbean, where some countries like Antigua and Barbuda turn a blind eye to their sportsbooks offering their services in the US.
How legalized gambling markets combat illegal betting across the globe
Despite all the issues with illegal betting listed above, the governments and international AML and sports integrity organizations become more aware of the problem and do their best to combat illicit gambling activities. Major sportsbooks, gambling associations, and betting authorities try to cooperate to minimize the risk of illegal betting. The level of cooperation, however, differs depending on the region.
So, let us see how different regions tackle the problem of black-market betting.
European market
In Europe, sports betting accounts for the majority of gross gaming revenue, generating 40% of the gambling profits. Most of the EU countries have legalized sports betting and the number of regulated sportsbooks is only going to increase over the years.
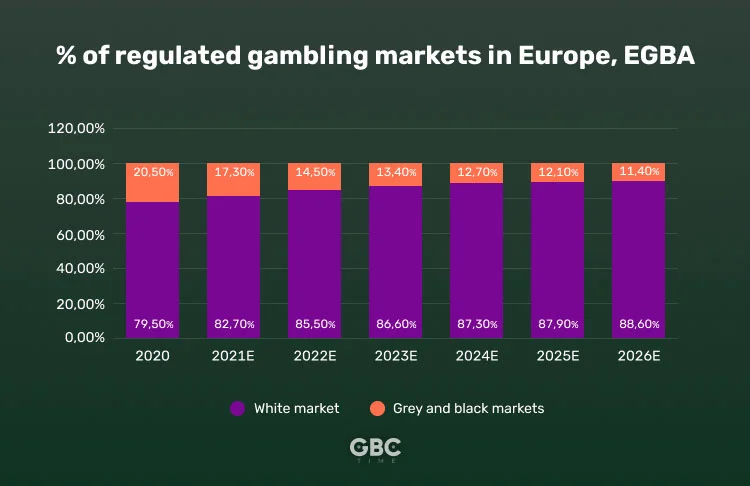
To give an advantage to legal sportsbooks, the majority of EU states have adopted liberal sports betting laws. This also allows to dry illegal markets and minimizes the threats to the public health and sports integrity, presented by black-market ops.
To safeguard their players and address money-laundering threats, betting authorities require new customers to go through various identity verifications and AML checks. At the same time, the majority of AML, Know-Your-Customer (KYC), and monitoring policies are written in a recommendation manner.
The EU authorities also understand the threat posed by the wide use of cryptocurrencies in betting. That is why the European Parliament has recently approved a draft regulation, MiCA, on digital assets.
At the same time, the European betting market still has too many black market sportsbook providers, the growth which is stipulated by the tight gambling laws of some countries.
The US market
In the US the situation is similar to the one in Europe. After the introduction of legal sports betting in 2018, the average spending on illegal sportsbooks dropped by 25%. The American Gaming Association has listed the following factors as the key elements that influenced consumer’s choices:
- Confidence that winnings will be paid out – 25% of respondents;
- Awareness about the legal options – 20% of surveyed people;
- Desire to bet with a legal sportsbook – 19% of those surveyed.
At the same time, many people still confuse legal and illegal offers. 55% of people that placed bets at black market sportsbooks believed they were gambling at the regulated sites. So, illicit operators often take advantage of the unknowing customers. Nonetheless, the demand for legal sportsbooks in the US has never been so grand.
As for offshore betting, it is illegal in the United States. To combat this, the US has approved the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act (UIGEA) prohibits American banks to pay into accounts of online gambling operators located outside of the US.
The illegal market is here to stay
While international organizations and local authorities try to combat illegal gambling at all costs, the black market will not magically fade away. It is vital to understand that unlicensed betting providers are here to stay. And here are a few reasons why.
Better odds and bonuses
Offshore and black-market sportsbooks provide better odds and bonuses than legal operators that are bonded by player protection requirements.
Anonymity
In regulated markets, to place a bet, players have to go through various identity verification, KYC, and AML checks. The level of anonymity at illegal sportsbooks is much higher – there are no credit card transactions, no tax forms, etc. This allows gamblers to keep their activity secret from spouses and family.
Provision of gambling on credit
Offshore gambling sites often allow customers to place bets with credit money. At the same time, many gambling jurisdictions like the UK or Spain ban gambling on credit.
No legal issues
Sportsbook operators that work in the white-market environment often face regulatory issues and fines for incompliances.
Bottom line
Black-market betting is becoming a significant problem for players and regulators all around the world. Governments, authorities, and legal betting providers cooperate to eliminate illegal betting, corruption, and money laundering in the gambling niche. At the same time, ineffective regulations could lead to a surge in black-market activity.
As the gambling consultant Richard Schuetz wrote:
“By creating the black market with a bad law, it could later be argued that the bad law then needed to be overturned to stop the black market.”
Read more: Betting Affiliate Programs